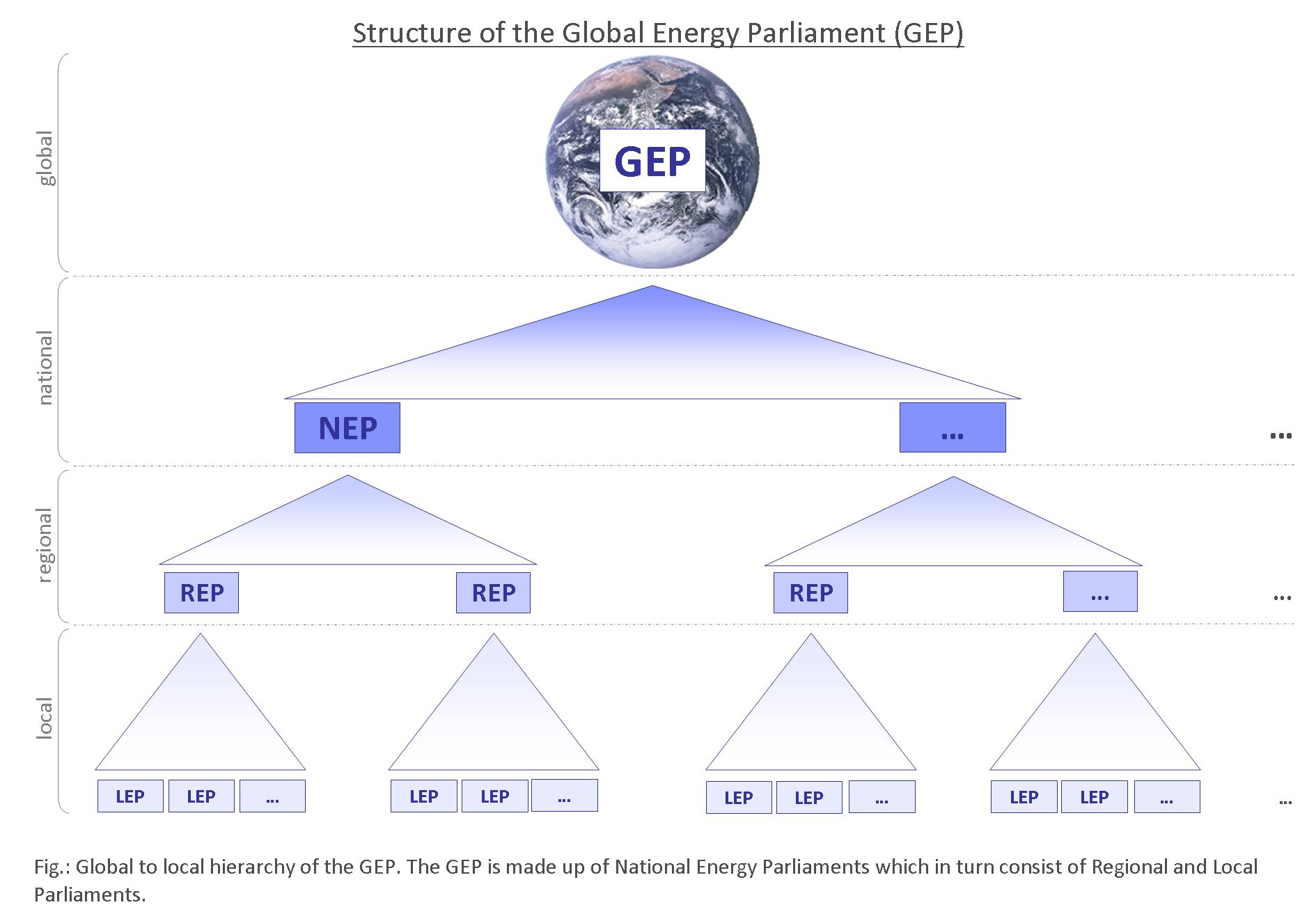
The Global Energy Parliament consists of National Energy Parliaments, which are fed by Regional Energy Parliaments, which in turn consist of Local Energy Parliaments.
Global Energy Parliament: concerns itself with international problems and decision-making at global level (ex: Solutions to the international economic crisis);
National Energy Parliaments: concerns with national problems (ex: German medical system), of which relevant recommendations and issues can be forwarded to GEP for discussion;
Regional Energy Parliaments: concerned with state and regional issues (ex: State of New York's decision on hydraulic fracturing) in a National Energy Parliament;
Local Energy Parliaments: concerned with activities that affect communities, towns, villages and local bodies (ex: neighbourhood tree-planting).
What they do:
Parliaments at each level provide policy leadership, funding, active research and recommendations submitted to elected governments, intra- and supra-national organisations.
How they work:
Regular sessions of Parliaments are held at least once annually, to identify and resolve current issues.
Who is involved:
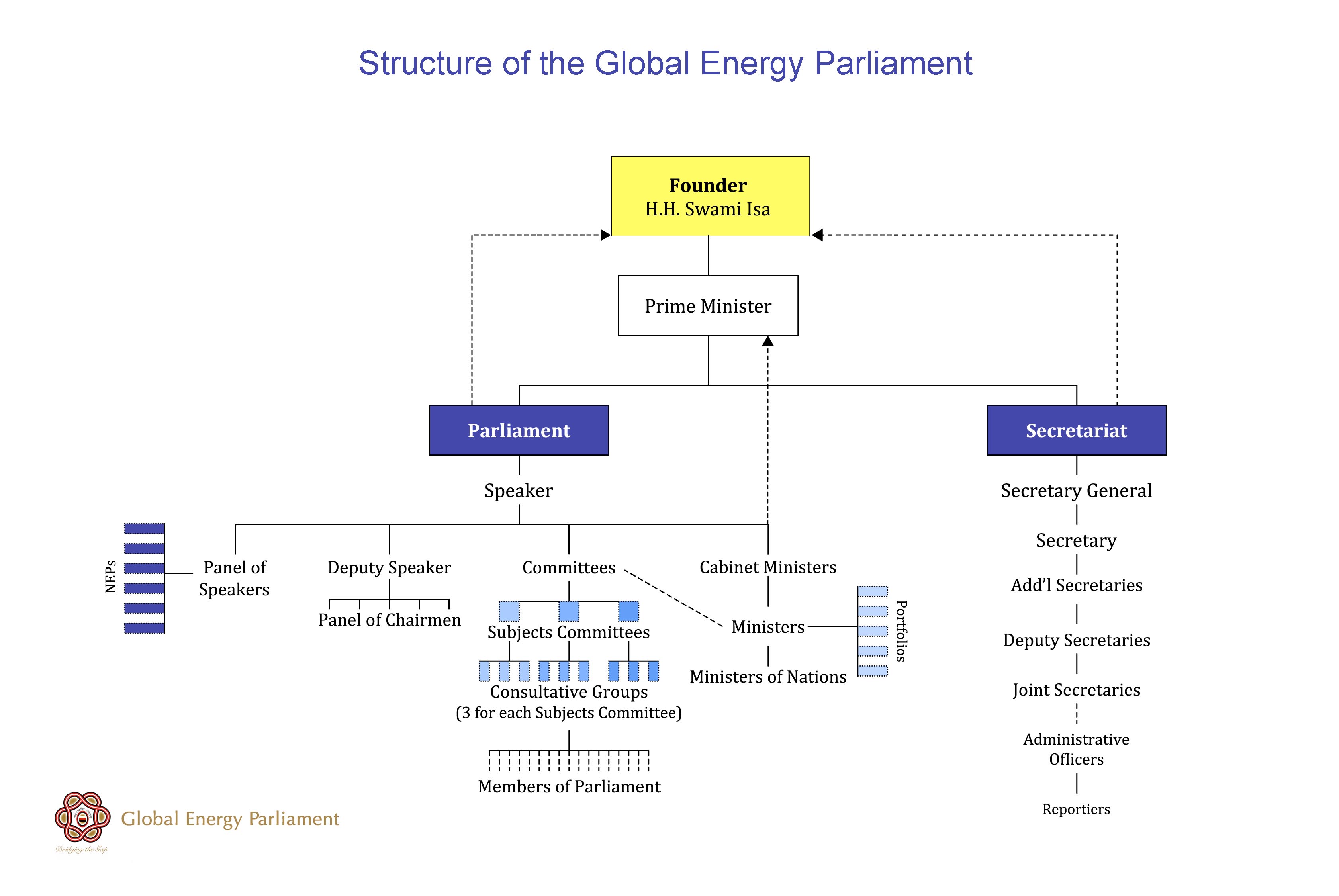
- Founder: The Founder of the GEP is H.H. Swami Isa, whose vision guides the GEP and its activities.
- Prime Minister: The Prime Minister oversees both the parliamentary and the administrative arms of the Global Energy Parliament, and reports to the Founder.
- Secretary General: Each Parliament is supported by a Secretariat that carries out the administrative work, headed by a Secretary General. There is no limit on the length of appointment in this position. He or she reports to the Prime Minister and Founder. Reporting to the Secretary General are Additional Secretary, Deputy Secretary, Joint Secretary, etc. (Refer to diagram, below).
- Speaker: The head of the Parliament is the Speaker, who is elected by the body and generally holds office for one year. He or she reports to the Prime Minister and the Founder. The Speaker is directly involved with the programming and conduct of the session of Parliament; ensuring that the discussions reach conclusion; that Members are heard; that Committees are on task; and that Recommendations are forwarded to the appropriate bodies.
The Speaker of an NEP, REP and LEP holds a seat in the next-higher level of Parliament by participating on the "Panel of Speakers". Under the Speaker are the Deputy Speaker, Committees, Panel of Speakers and Ministers.
- Panel of Speakers: Consists of the Speaker of each Parliament falling under the current Parliament (ex: at the Global Parliament, consisting of the British Speaker, French Speaker, Japanese Speaker, etc.) Responsible for representing their Parliament and carrying out decisions coming from higher level.
- Deputy Speaker: Assists the Speaker in all matters, and acts in the role of the Speaker in his or her absence. Holds office for one year.
- Committees: Committees are constituted by the Speaker, and consist of Members and Ministers. They are divided into Subjects Committees and further into Consultative Groups. (ex: Subjects Committee on the Alternative Energy Sources; Consultative Groups on Solar Energy; Sound Energy; Wind Energy). Each Member of Parliament will serve on one or more Committee.
- Cabinet of Ministers: comprised of the top-level Ministers. Holds office for one year.
- Ministers: Ministers are appointed by the Prime Minister and have a specific Portfolio relating to their area of expertise, such as Health or Education. GEP Ministers are not political persons per se, but rather those who have demonstrated keen insight and leadership in their chosen field. Ministers have insight into the main issues in their field that are affecting their region. They provide leadership to implement procedures, policies and recommendations of Parliament, and the Secretariat supports their work. Holds office for one year.
Members: Members are invited or appointed to serve on one or more of these levels of Parliament. Members of Parliament are involved in proposing, considering and voting on new recommendations. Within their area of expertise, Members can also participate on Consultative Groups or Subjects Committees. Read more about Membership in the GEP.